Underground deposits : witnesses to the environments of the past
UNDERGROUND RIVERS AND WATER SEEPAGE DEPOSIT SEDIMENTS IN CAVES : PEBBLES, SAND, CLAY, STALACTITES AND STALAGMITES. The nature and types of these deposits offer a valuable source of information on the mechanisms of the development of ancient environments : palaeoclimates, plant cover in the past. In addition, the ability to date stalagmites allows us to assign them their correct place in the great geological calendar.
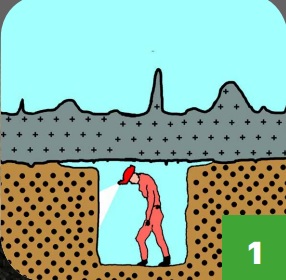
FIG 1 A river deposits sand in the gallery. The gallery dries out, stalagmitic concretions grow on the sand.
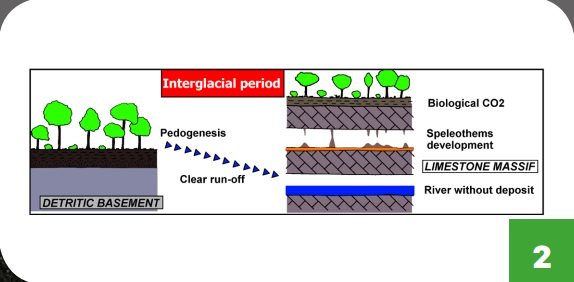
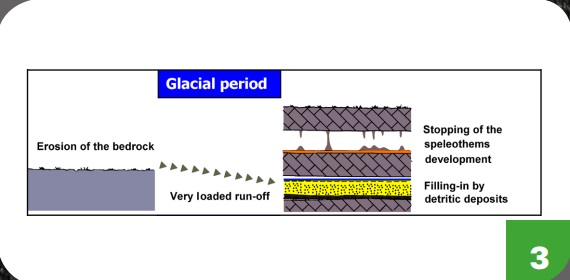
Links between underground deposits and climate.
FIG 2 Hot, humid period : interglacial. Abundant CO2 in soils, created by life forms, makes seepage water acidic. As a result, it contains high concentrations of dissolved lime stone and precipitates large quantities of calcite to form concretions.
FIG 3 Ice age. Lack of vegetation (tundra landscapes) plus freezing cause soil erosion. Rivers are full of debris, some of which is deposited in caves.